smart board dimensions: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
Smart boards have revolutionized the way we interact with information and technology in various educational and professional settings. Understanding the dimensions of a smart board is crucial to ensure compatibility and optimal usage. In this article, we will explore the different aspects of smart board dimensions, including size, aspect ratio, resolution, and more.
1. Size Matters: Choosing the Right Dimension
When it comes to smart boards, size does matter. The size of a smart board refers to its diagonal measurement, typically expressed in inches. Smart boards are available in a range of sizes, from compact 55-inch models to large 98-inch ones. The ideal size for your smart board depends on the intended use and the size of the room where it will be installed.
Smaller smart boards, such as 55 or 65 inches, are suitable for small meeting rooms or classrooms with limited space. On the other hand, larger smart boards, like 86 or 98 inches, are perfect for larger conference rooms or auditoriums.
2. Aspect Ratio: Finding the Right Proportions
The aspect ratio of a smart board refers to the proportional relationship between its width and height. The most common aspect ratios for smart boards are 16:9 and 4:3.
A 16:9 aspect ratio is commonly found in modern smart boards and is suitable for multimedia presentations, videos, and widescreen content. On the other hand, a 4:3 aspect ratio is more traditional and is often used for displaying documents and presentations in a more square-like format.
3. Resolution: The Clarity of Visuals
The resolution of a smart board determines the level of detail and clarity of the displayed content. It refers to the number of pixels that make up the screen. The higher the resolution, the sharper and more vibrant the visuals.
Common resolutions for smart boards include Full HD (1920x1080 pixels), 4K Ultra HD (3840x2160 pixels), and even higher resolutions for advanced models. Choosing a smart board with a higher resolution is recommended, especially if you plan to display high-definition videos, images, or intricate content.
4. Touch Technology: Interacting with Precision
Smart boards are known for their touch functionality, allowing users to interact with the displayed content using their fingers or a stylus. The touch technology used in smart boards can affect the overall user experience and precision.
There are two main types of touch technologies used in smart boards: resistive and capacitive. Resistive touch screens are pressure-sensitive and require slight pressure to register touch, while capacitive touch screens respond to the electrical charge of the human body.
5. Connectivity Options: Seamless Integration
Smart boards offer various connectivity options to ensure seamless integration with other devices and systems. These options include HDMI, VGA, USB, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi.
HDMI and VGA ports allow you to connect your smart board to computers, laptops, or other external devices. USB ports can be used to connect peripherals like keyboards, mice, or storage devices. Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity enable wireless screen mirroring and collaborative features.
6. Installation: Wall-Mounted or Free-Standing
Smart boards can be installed in two main ways: wall-mounted or free-standing. The installation method depends on the available space and the preferences of the users.
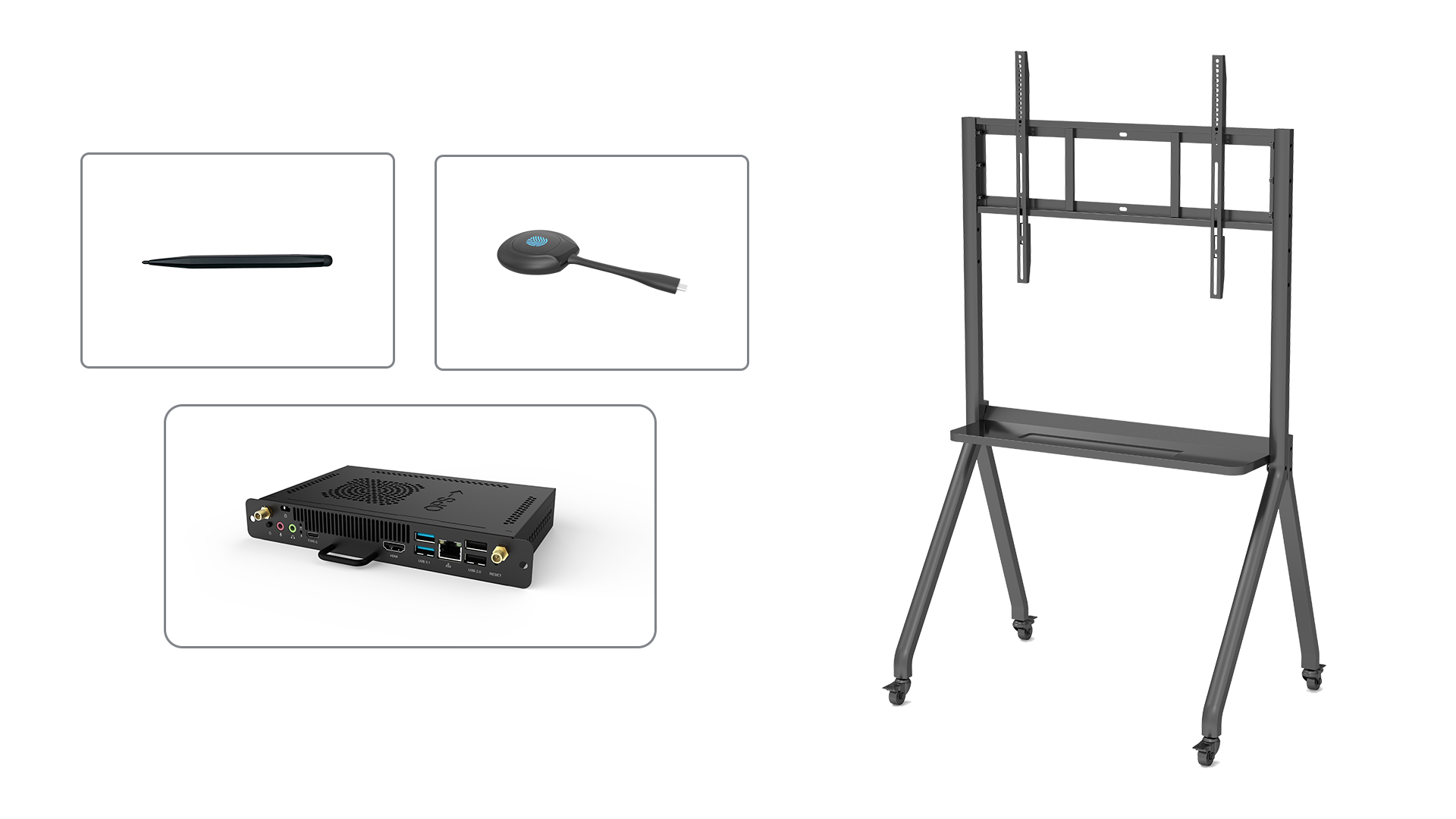
Wall-mounted smart boards are fixed to a wall using mounting brackets, which provide stability and save space. Free-standing smart boards, also known as mobile or portable smart boards, come with built-in stands or wheels, allowing for easy movement between different locations.
7. Weight and Portability: Considering Mobility
The weight of a smart board is an important factor to consider, especially if you plan to move or transport it frequently. Lightweight smart boards are easier to handle and transport.
Additionally, portable smart boards with wheels or handles provide enhanced mobility, making them suitable for environments where flexibility is required, such as trade shows or temporary setups.
8. Accessories and Enhancements: Expanding Capabilities
Smart boards can be enhanced with a variety of accessories to expand their capabilities and offer a more immersive experience. These accessories include interactive pens, wireless presenters, document cameras, and audio systems.
Interactive pens allow users to write, draw, or annotate directly on the smart board's surface. Wireless presenters enable seamless control of presentations from a distance. Document cameras capture and display real-time images or documents. Audio systems enhance the sound quality for a more engaging multimedia experience.
9. Maintenance and Durability: Longevity Matters
Proper maintenance and durability are essential for the longevity of a smart board. Regular cleaning using non-abrasive materials and avoiding excessive pressure while interacting with the board can help prevent scratches or damage to the surface.
Additionally, choosing a smart board with a durable build, such as one with a tempered glass surface or a robust frame, can ensure it withstands daily use and occasional accidental impacts.
10. Cost Considerations: Balancing Budget and Quality
Finally, cost is an important consideration when selecting a smart board. The price of a smart board depends on various factors, including size, resolution, touch technology, and additional features.
While it is tempting to opt for the most advanced and feature-rich smart board, it is crucial to balance the budget and the actual requirements. Assessing the needs of the users and prioritizing essential features can help find the right balance between cost and quality.