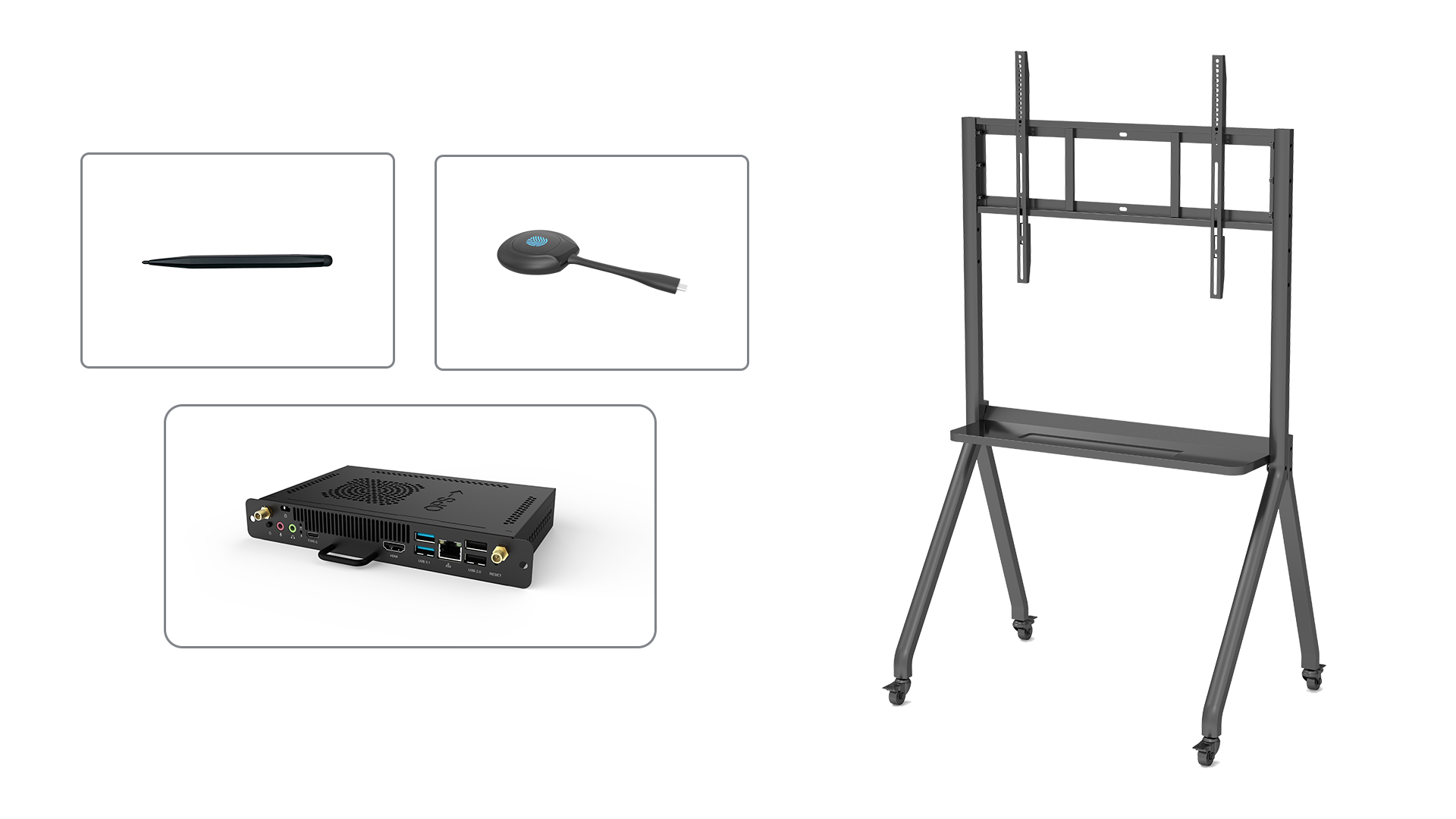
Numerous multinational corporations discovered that they were nevertheless able to function effectively and profitably throughout the Covid-19 outbreak despite an unanticipated and nearly full evacuation of staff from their headquarters. The digitization of routine jobs and activities has improved customer service, customer communication, and information processing. The use of online communication in place of everyday face-to-face encounters was well received by the workforce. The executives of these multinational corporations thus started to reconsider their organizational structures.
Large-scale remote labor, however, comes with both potential and difficulties. Businesses who are able to effectively utilize these advantages may obtain a competitive edge. However, to do this, companies' structure must shift.
According to our survey, considering two factors, that is, whether companies choose to hire employees in some countries (low degree of internationalization) or in many countries (high degree of internationalization), the work modes of international enterprises can be divided into four types.
1. Large-scale central: that is, a low degree of internationalization, relational task environment background.
For example, a highly knowledge-intensive international professional services firm such as an architecture firm might centrally deploy all of its engineering, drafting and design development in a central location at each prime location. These are office-centric, as employees must work closely together to complete specialized, knowledge-intensive or creative activities. Such organizations are tightly structured in the few countries with large centres staffed to stimulate creativity and innovation, perhaps thanks to knowledge clusters or centres of excellence. Some interactive remote work is available, but only close to the center. People expect frequent collaborations by showing up in the office.
2. Center plus satellite point type: that is, a high degree of internationalization and a relational task environment background
It is also office-centric, relying primarily on key centers around the world, but also supplemented by satellite-style operations to take advantage of smaller clusters of knowledge workers or regional clusters of expertise. For example, professional services business leaders we interviewed used satellite offices to address local needs by combining local expertise with a global perspective.
3. Decentralized: that is, a low degree of internationalization, transactional task environment background
In the mode, most tasks are routine tasks with high workload and thus are easy to digitize. Therefore, enterprises are suitable for decentralized layout. This work mode greatly requires the METZ interactive collaboration display for better workplace communication. Typically, this mode of work extends to at least a few countries, but not beyond that. If necessary, the company's products can enter the wider market without the company's presence.
4. Global virtual: that is, a highly internationalized, transactional task environment background
The model allows for talent acquisition on a global scale. This model is not motivated by the search for specific talent or favorable labor costs, and is ideal for businesses that require the global nature of their business, yet succeed with only a small number of employees in each country. In this model, employees in many countries work together as a global but virtual enterprise, interacting with each other across geographic boundaries. For smooth and convenient communication, interactive smart panel displays are indispensable, and physical offices will not have too much great value.
So, what kind of hybrid work model is right for your company? Whether you need a better collaborative office.